 Taste (gustation).
Taste (gustation).
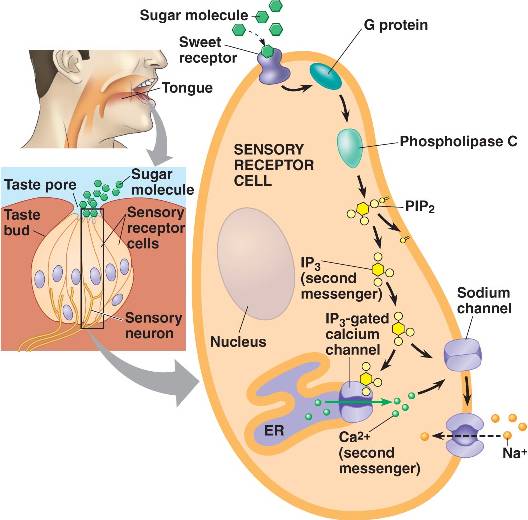
The receptor cells for taste are modified epithelial cells organized into taste buds, which are scattered on the tongue.
Binding of a sugar molecule to a receptor cell initiates a signal transduction pathway.
Sodium channels open, Na+ ions diffuse into the cell, and the membrane depolarizes.
Nerve signals are then sent to the parietal lobe of the cerebrum.